Up to 2016, every purchase or service acquisition in India entailed the payment of various taxes such as VAT and Service Tax. A year later, the introduction of GST (the Goods and Service Tax) revolutionised our intricate taxation system, simplifying and unifying the process by subsuming multiple taxes under one umbrella. However, even after this transformation, a persistent question might linger: does GST apply to international money transfers, commonly referred to as inward remittances? As a business operating in India, how do you go about GST for foreign exchange?
The debate on this matter ultimately concerns whether India levies taxes on international money transfers. Taxing inward remittances received by businesses could contribute to the nation's revenue, potentially bolstering its financial resources.
However, this idea has its complexities and implications, as it may impact the livelihoods of those who rely on remittances from family members working abroad. Let's try to answer this question and get a detailed understanding of how GST for foreign exchange works.
Should I Charge GST to Foreign Clients?
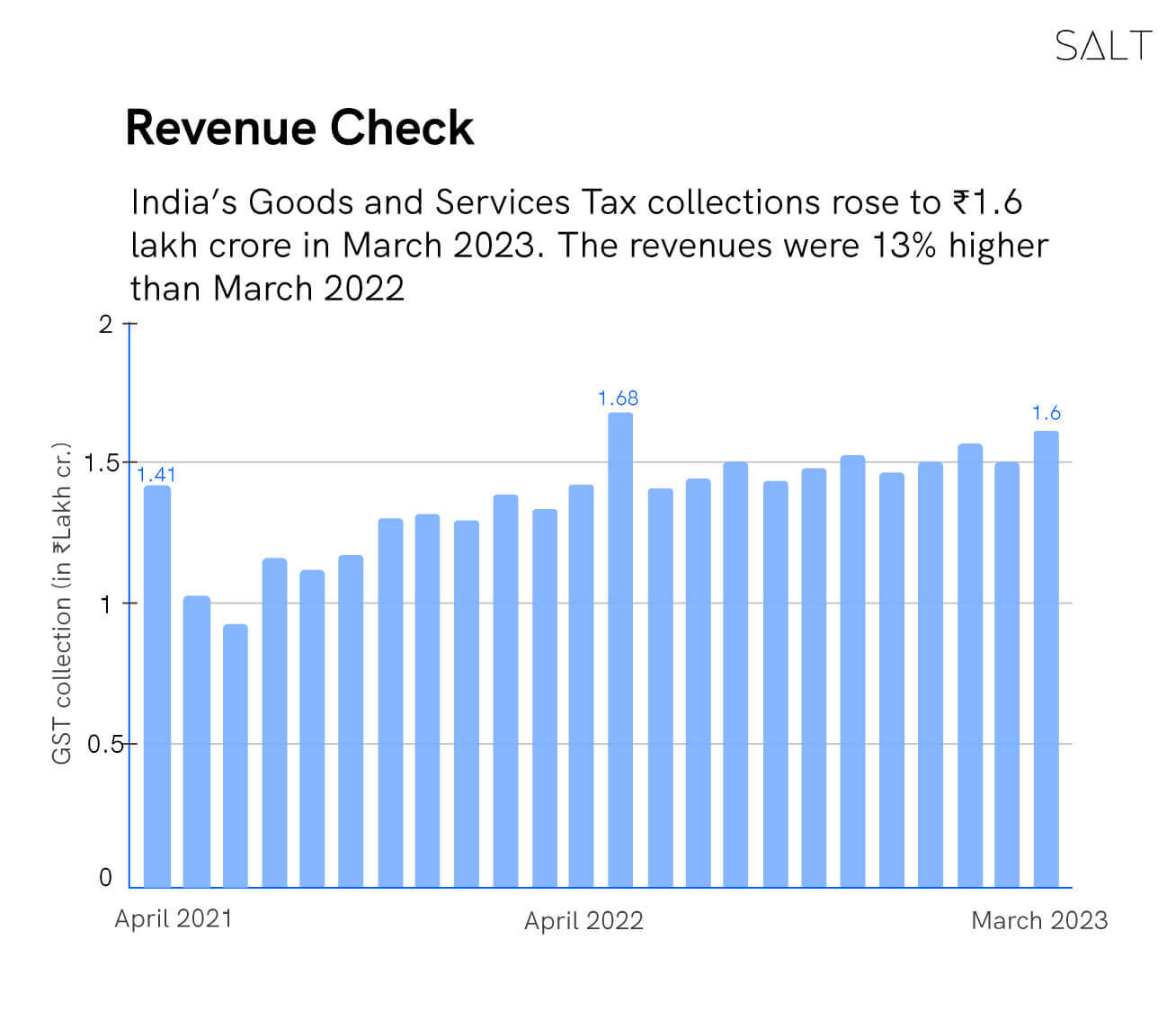
GST is a significant source of income for our economy, with the Goods and Services Tax revenues having grown by 13% in March, 2023. Interestingly, this was the second highest monthly collections recorded from the indirect tax since its inception, standing at ₹1.6 lakh. Further, receipts from imports rose by 8%, and income from both domestic transactions and services imports have risen by 14% since last year.
As a GST-registered business in India, you are required to charge GST for inter-state trades, and must produce GST-compliant invoices for such transactions.
Now, coming to GST for foreign exchanges. The clear answer would be that GST typically does not need to be charged to any foreign clients you are dealing with. However, the tax may be applicable to any fees or charges associated with the money transfer service, such as service charges or foreign exchange conversion fees, which are considered taxable services under GST regulations .
GST for Foreign Exchange: Implications
When it comes to GST for foreign exchange, when are GST regulations involved? Let's find out.
GST on Inward Remittances
When it comes to receiving foreign currency through inward remittances in India, GST typically does not apply separately. Even though international money transfers online may incur an 18% transaction fee for certain products, this fee does not translate to a separate GST charge on the remittance itself. This is a significant benefit for businesses dealing with foreign clients because they do not need to add GST as an additional tax when providing their services.
GST regulations apply to services like compliance handling and the issuance of Foreign Inward Remittance Certificates (FIRCs) and Bank Realisation Certificates (BRC) in India. However, what makes this scenario unique is the application of the reverse charge mechanism. Under the reverse charge mechanism, the responsibility for paying GST directly to the Indian government falls upon foreign clients, relieving the service provider's business from this financial obligation.
Consequently, there is no need to itemise or separately charge GST on invoices when providing these services to foreign clients. This streamlined approach simplifies the billing process for both the service provider and international clients.
Consider a scenario where a company assists a foreign client with compliance issues. Through the reverse charge mechanism, the foreign client assumes the responsibility for remitting the GST to the Indian government, thus alleviating the service provider's business from this financial obligation.
GST on Forex Transactions
While we’re on the topic, let’s come to international money transfers in GST for foreign exchange. Foreign currency conversion transactions are subject to GST, and the value of service for the levying of GST in purchases/sales of foreign currency is determined as per the table in the figure below, upon which a GST of 18% is applicable.
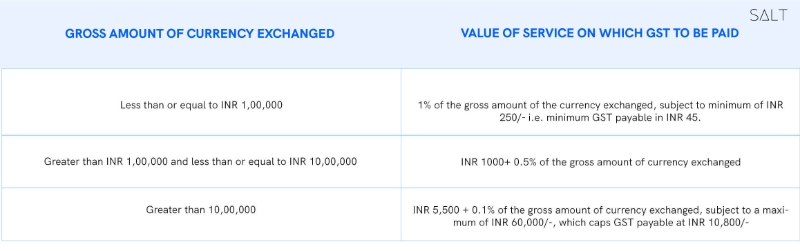
However, these transactions amongst banks or authorised dealers are exempt under GST regulations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, as a business operating in India, you are typically not required to charge GST on foreign exchange. However, GST applies to services like compliance handling and issuing FIRCs and BRCs in India. The unique aspect is the reverse charge mechanism in such cases, shifting GST payment responsibility to foreign clients. Service providers don't need to itemise or charge GST separately, simplifying billing for both parties.
Are you looking for a trusted global finance partner as you consider international expansion for your Indian business? Look no further than Salt Fintech, where we allow you to conduct global business and receive cross-border payments with local accounts. Further, SALT takes over compliance responsibilities for you too, making international money transfer the easiest part of your business.
Give us a visit today to learn more!
For additional insights and expert opinions on international business, cross-border payments, and taxation, visit the Salt blog.
FAQs
Which foreign transactions are GST applicable to?
Here is a list of the categories of international money transfers GST regulations apply to:
Export of goods by payment of IGST or under LUT/Bond
Export of services
Import of goods, which is governed by the Customs Act, 1962
Import of services for business or non-business purpose
Sale and purchase of goods without the said goods entering India
Supply of goods before clearance for home usage
OIDAR or Online Information Database Access and Retrieval services (for business or non-business purpose)
What are the requirements for a GST registration for my business?
If your annual aggregate turnover to Indian and foreign clients combined is over ₹20 lakhs, you need to get registered under GST regulations. However, aside from this mandate, you can register for GST on your own early on.


