What is the Swift message system?
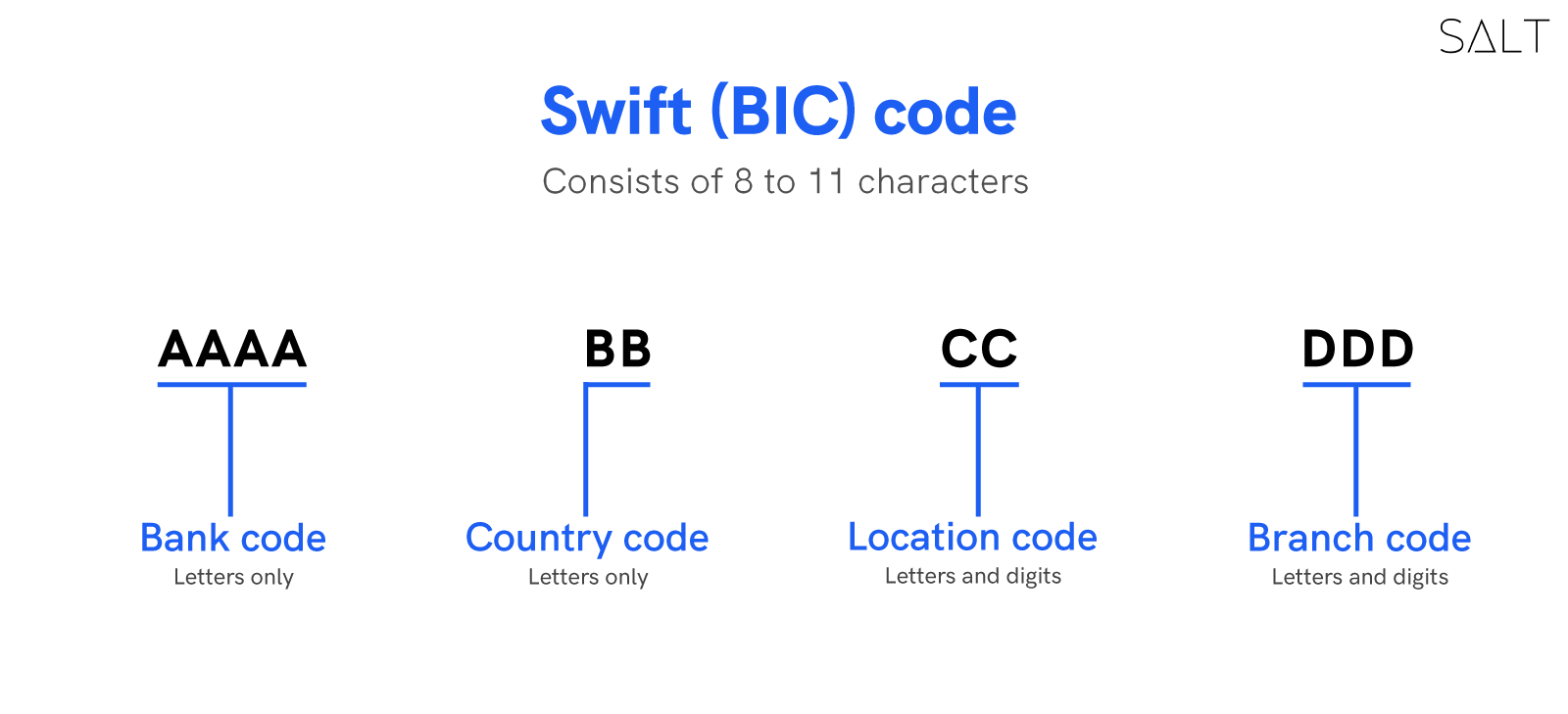
The "Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication" is known as SWIFT. Over 8,300 banks, securities firms, and businesses in over 208 countries are part of the SWIFT network. The SWIFT code is a Business Identification Code (BIC) that SWIFT assigns to banks as a simple means of making international payments.
Prior to SWIFT, all banking communications were conducted by phone, telex, mail, or courier. With the advent of SWIFT, messages between banks may now include messages and conditions in addition to the fundamental instructions for transferring payments. Each SWIFT message is needed for wire transfers.
The SWIFT code is used for all international transactions carried out by this bank. The code's function is to serve as a universal digital language for easy international money transactions.
The idea makes for a simple, quick process. To get the code and join the network, a bank must opt into SWIFT payment. This enormous system is electronic and sends and receives codes across banks swiftly using a cloud platform.
How does the SWIFT message system work for businesses?
With the help of SWIFT, businesses, financial institutions, and banks may communicate with one another and cooperate with banks around the world and in their neighbourhood.
As a result of the standardization of such messaging, both banks and their clients can benefit from consistent rules and procedures across numerous banks.
SWIFT just helps banks communicate with one another; it is not a bank and neither holds money nor keeps accounts.
With the help of SWIFT, banks now have access to a centralized database that makes it possible for Bank A to securely communicate with Bank B without having to rely on human intermediaries or expose themselves to the risks associated with using email, phone, or fax. The SWIFT communication network is very dependable and secure.
There are different categories and formats of SWIFT messages for different businesses.
Format :
Categories
What is a purpose code?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) created the purpose code to categorize each transaction according to its nature as a foreign currency transaction. To put it another way, the Purpose Code aids regulators in determining the precise nature of a cross-border transaction.
Therefore, in India, it is required for all cross-border payments. The two types of purpose codes are as follows:
1. Payments received by Indians in foreign currency for receipt purposes or the purpose code for inward remittance.
2. Payments sent by Indians or outward remittances in foreign currency.
How do businesses use purpose codes?
The purpose code aids regulators in figuring out the specifics of a cross-border transaction. When executing a transfer, you must provide the code P0301 if the goal of your international transaction is, for instance, "purchases for travel."
Every remittance must include one of the purpose codes that the RBI has established in order to describe the nature of the transaction and the unique purpose for which the transfer is being made. The RBI can categorize transfers thanks to these codes.
Every remittance must include one of the purpose codes that the RBI has established in order to describe the nature of the transaction and the unique purpose for which the transfer is being made.
Remittances can be classified by the RBI using these codes. Given that India is the country that receives the most inward remittances worldwide, it makes sense that purpose codes are crucial there.
A list of some purpose codes
SALT in International Payments
India and many other nations require purpose codes for cross-border payments since they make transactions easier and more convenient.
SALT fintech allows you to transfer money internationally within 24 hours for a fee of just 1.75% of the entire transaction value. SALT has no minimum transaction requirement, regardless of whether you are a startup or a SME. When utilizing SALT, there are no extra fees, annual subscription costs, or markup costs.
Everything is more affordable and efficient with SALT.


