What is the difference between SWIFT and Local Transactions?
When it comes to transferring a payment, you have a range of options at your disposal, very prominent among them being SWIFT transfers and local transactions. Which one should you choose between the two? That’s exactly what we discuss in this pos
What is SWIFT?
SWIFT is the shortened version of Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication. It is an organisation that standardises international financial transactions. It was established when banks worldwide required a reliable, uniform method for international money transfers.
It's a frequent misperception that the SWIFT network acts as a portal for cross border payments; in reality, it uses SWIFT codes or BIC (Bank Identifier Codes) to convey information and payment requests between financial institutions.
The SWIFT International Payment network is a safe, computerised, worldwide system for payments and settlements. A SWIFT wire transfer is initiated by the payer's bank debiting their account, and it is completed by the recipient's bank crediting their account after passing through many intermediary banks in the SWIFT network. The largest financial communications system in the world is this type of telegraphic transfer (TT), also sometimes referred to as a wire transfer. The SWIFT network is the most widely used infrastructure for international money transfers and the largest financial messaging system in the world.
Read a detailed blog on how does SWIFT payments work.
What Are Local Transfers?
Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS) and other electronic local payment systems are used for local transfers. To transfer money to the local bank account of the remittance provider in the sending currency, the customer utilises a domestic transfer. The remittance provider handles the FX conversion through its network, and the converted amount is paid at a pre-set rate in the destination currency.
In the past, telegraphic transfers (TT) or SWIFT transfers were frequently used for international money transfers. However, local transfers are now becoming more popular due to the significant benefits they provide to end users. Local bank transfers let you pay someone using their local bank through a network of international financial institutions. The method eliminates the need for middlemen banks by using a global network of bank accounts in local currencies to settle bank transfer payments (also known as remittances) between the two parties.
Requirements For SWIFT Transfers And Local Transactions
A SWIFT code, a special string of 8–11 characters used to identify the particular bank to which your funds are being transferred, is necessary for SWIFT transactions. This means that to facilitate the transfer of SWIFT codes, all concerned financial institutions must be a part of the SWIFT network.
Instead of using conventional banking networks that handle SWIFT transfers, local bank transfers only require the recipient's bank account information and a reference number.
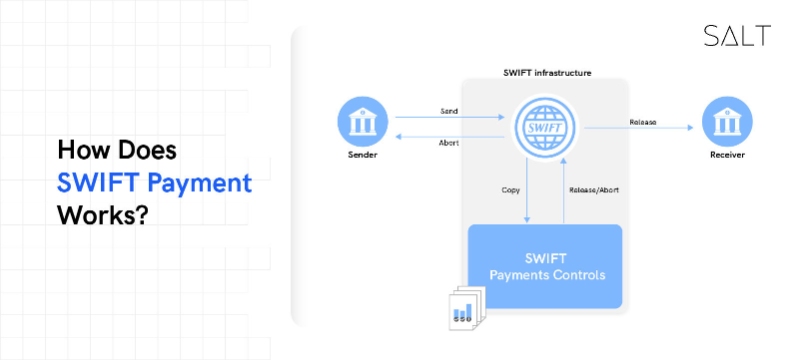
How much does a SWIFT transfer cost?
Due to fees that might be assessed by both correspondent and recipient banks, the complexity of SWIFT transfers frequently leads to greater expenses. When you transfer money between banks in different countries, each intermediary bank levies a processing fee or commission. Additionally, there is no set fee schedule due to the SWIFT payment network's global reach. When transferring sizable amounts of money that local channels cannot handle, SWIFT is more advantageous. The fee for a SWIFT transfer is determined by the specific bank or financial institution handling the transaction.
Typically, there are two types of fees involved: transactional charges and exchange rates. The transfer and receiver fees are also included in the costs; each bank typically fixes these prices. In some circumstances, if an intermediate bank is used to transfer the money, you can additionally be charged a "correspondent bank fee." In an emergency, you can always pay a priority payment fee to shorten the time it takes to process your payment. As for the exchange rate, the quantity of money you want to send will also affect the exchange rate that is charged.
Which Method Is Better: SWIFT or Local Transactions?
After being well-versed in each bank transfer technique, now you need to pick the one that better suits your needs. You should of course take time into account while making a transfer. It is preferable to use a SWIFT wire transfer if the speed and timing of the transfer are crucial to the customer according to their circumstances.
However, the key benefit of local transfers over SWIFT transfers is that there are no additional hidden costs. A local bank transfer also has lower fees because it saves the client money on foreign exchange rates and other expenses related to other cross-border transfer methods. However, the transfer's initiating country must be where the receiving currency is used.
The extent of SWIFT and Local Transactions
Over 10,000 financial institutions in 212 nations are connected securely through SWIFT, which says a lot about SWIFT’s credibility. On the other hand, due to their convenience, local bank transfers are quickly gaining popularity worldwide. Through a strong network of regional banks and payment processors, the customer can contact just about anyone worldwide. However, only the currencies supported by their network may be allowed when working with cross-border remittance providers.
To sum up, here’s your requirements for both kinds of transfers, and other features to keep in mind, in brief:
Conclusion
Nearly 50% of all global cross border payments are made through SWIFT transfers, an established and trustworthy bank transfer technique. While going for a local transfer, make sure to remember to ensure that all transactions are carried out safely and securely, it is crucial to use a bank governed by the local authority with the proper anti-money laundering and fraud checks.
Salt is a neobank dedicated to help you manage your global finances with the convenience of local accounts. Want to find out more about us and what we do? Give our website a visit today!


