All of us are aware of the direct transfer of funds our banks initiate in cases of recurring bills, subscriptions, and membership fees. That very system of transfer is called ACH or Automated Clearing House in the US. ACH is a network that handles electronic payments and transactions, including direct deposits. This payment system solved the issue of rigorous sorting and processing of paper checks in the US and revolutionised the money transfer system.
But does ACH work in India? Read to find out.
Contents
Do Indian banks support ACH?
ACH transactions are a US-exclusive concept, and therefore Indian banks can’t support ACH. However, the concept of ACH exists in India - it is better understood as ECS or Electronic Clearing Service here.
ECS is an electronic payment mode used for repetitive payments and is periodic in nature. It is largely used by organisations to roll out their bulk payments, especially salaries, pensions, interest, etc. Individuals use this mode of payment to settle dues for electricity, water and other recurring bills, along with loan instalments and periodic investments.
ACH facilitates the transfer of funds directly from one bank to another, eradicating the manual procedures that used to be followed.
ACH Transfer Money To India
Both Individuals and Merchants can ACH transfer money from USA to India. It usually takes 2-3 days to deduct money from your US bank account and transfer it to your Indian bank account. You may open a virtual local bank account in the US using services like Salt, Wise, etc. You can ACH transfer international money in your US virtual bank account, which gets immediately transferred to your INR Bank a/c.
How do ACH payments work?
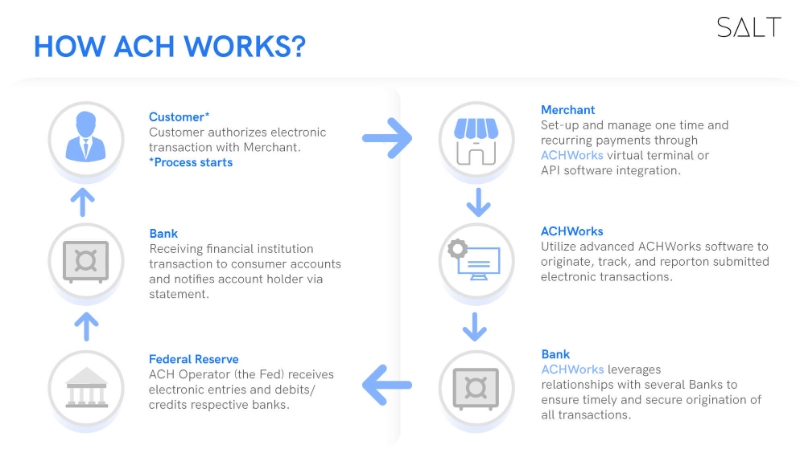
In order to understand the various kinds of ACH payments or their benefits, it is pivotal to understand how the process of ACH works.
ACHs are electronic payments where funds move from one bank account to another through an intermediary, which helps route the money to the desired location. It facilitates direct bank-to-bank payment and includes personal as well as business transactions. Any payment made by one person to another or to any business digitally is included in ACH transactions. Any ACH transaction needs several parties to be involved:
The Originator: The originator is the person who initiates a payment request.
The Originator’s financial institution: The Originating Depository Financial Institution (ODFI) refers to the bank where the originator has their account.
An ACH operator
The receiver’s financial institution: The Receiving Depository Financial Institution (RDFI) refers to the bank where the receiver has their account.
The Receiver: The receiver is the person who is meant to receive the payment on the other side.
Types of ACH payments
Primarily, there are two types of ACH payments:
Credit Transfer:
ACH Credit refers to the payments where one ‘pushes’ out money from their account to other bank accounts in different financial institutions. It includes non-urgent business-to-business payments and any payment made by retail customers. It also refers to a situation where an organisation rolls out the monthly salaries or pensions to the employees, or the dividends to the shareholders, or more.
Direct debit payment:
ACH Debit refers to the payments where the money is ‘pulled’ out of your account and transferred to another without intervention. Such transactions include utility dues, insurance premiums, interests, mortgages, etc. It also includes recurring bill payments where the authority to pull out the due from the account is given to the company that is to be paid. Hence, the amount gets deducted automatically every month.
Benefits of ACH payments
ACH transactions come with their own set of advantages that include:
Convenience:
A regular cheque payment takes considerable time to get delivered, followed by submitting and getting it cleared, where there are high chances of paper cheques being misplaced and faulty entries in the system. ACH has removed this labour-intensive process and made it easy to transfer domestic payments without hassle. Such transactions are quicker in nature and have made the entire process easy.
Lower fee for the merchant:
With other cashless payment methods like cards, merchants are charged a considerable percentage by card issuers. However, ACH payment reduces that fee to nearly negligible, making it easier for everyone to push funds from one place to another.
Relatively safer:
Another aspect that makes ACH payments stand out is the safety and security it offers regarding data protection. When a payment is made through the ACH process, all information related to the bank account is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Autopilot:
ACH provides multiple ways to make the payment process as easier as possible. One such service is automatic ACH payment. It means that once you allow automatic payments from your account, any and all recurring payments take place automatically, and you don’t need to keep an eye on the deadlines. The company that is to be paid will pull out the dues from your account on its own.
Long-distance payment:
ACH transactions help businesses settle bills in as little time as possible despite long distances, making B2B interactions and trades easier.
Reversible:
ACH payments are reversible under certain circumstances, but it is best to avoid them as much as possible.
Conclusion
Though ACH payments are a USA-exclusive concept, there is a very similar service in India called the ECS or Electronic Clearing System, which allows bulk payments as well as repetitive bills. The ACH has its advantages that help make the transfer process hassle-free. ACH transactions have made recurring payments extremely easy and less time consuming than ever before for those in the US.
Looking for an easy and comfortable way to manage global banking with local accounts as a small business in India? We at the Salt neobank have got you covered!


