The risks and rewards of international transactions don’t come without a cost to any organization. There’s the foreign currency risk, there’s political risks, among the many other threats to firms involved in international financing.
Because of these factors, it can get difficult for certain businesses to maintain a steady flow of income at all times. This post will discuss ways businesses might mitigate the effects of the dangers inherent in doing business on a global scale.
First - What are International Transactions?
international transactions are a cross-border commercial arrangement or credit operation that must be settled in a foreign currency. Investments are often made by businesses in purchasing, selling, or leasing physical or intangible property; lending or borrowing money; or any other transaction that may affect the relevant businesses' earnings, income, losses, or assets. All of these transactions quality as international transactions.
The transaction, and frankly the concept as a whole, exists because of an understanding between businesses that are connected in some way. And with that, comes risk. Let’s start with one of the most important risk factors in such engagements.
Foreign Currency Transaction Risk
Transaction risk is the potential negative impact of unfavorable changes in foreign currency rates on a closed transaction before settlement. This is the risk of a fluctuating exchange rate or currency that arises from the lag time between making a transactional commitment and having it finalized. It represents a kind of foreign exchange risk. When more time passes between the start of a contract or trade and its transaction, the potential for loss increases.
Derivatives, such as futures and options contracts, are used to hedge transaction risk by reducing exposure to fluctuations in the value of one currency relative to another over a short period.
How to Manage Transactional Risk
Central banks, particularly investment banks, engage in many currency transactions daily, which provide valuable clues. These financial institutions have established procedures to reduce exposure to transactional risk. Credit and market risks are often coordinated with them, and control over the complete risk management infrastructure is vested in a single authority figure. Although there isn't always agreement on who in the company is responsible for assessing transactional risk, it's usually someone in the credit or country risk departments.
Generally, banks will give a country rating that accounts for the whole scope of risks involved with lending in that country's currency, domestically and internationally. To emphasize, these ratings, notably the "transactional risk rating," play a significant role in defining the ceiling and exposure limitations for each market, taking into account the policies of the firms involved.
How to Mitigate Transaction Risk
Banks with transactional risk use money market and capital market products to hedge, such as currency swaps, futures, options, etc. Each hedging technique has pros and cons, and companies choose the appropriate instrument to cover their currency risk.
Using a forward contract FIRC, let's try to grasp a company's risk minimization. A company may fix the contract time rate and resolve it at the same rate. This ensures the firm's financial flow. This reduces rate volatility and improves decision-making.
A corporation may also enter a futures contract agreeing to buy/sell a particular currency; futures are more reputable and heavily controlled by the market, avoiding default. Options hedging is a fantastic technique to hedge rate risks since it requires less upfront capital and reduces adverse risk. Here are five strategies for lowering the international downsides of doing business abroad.
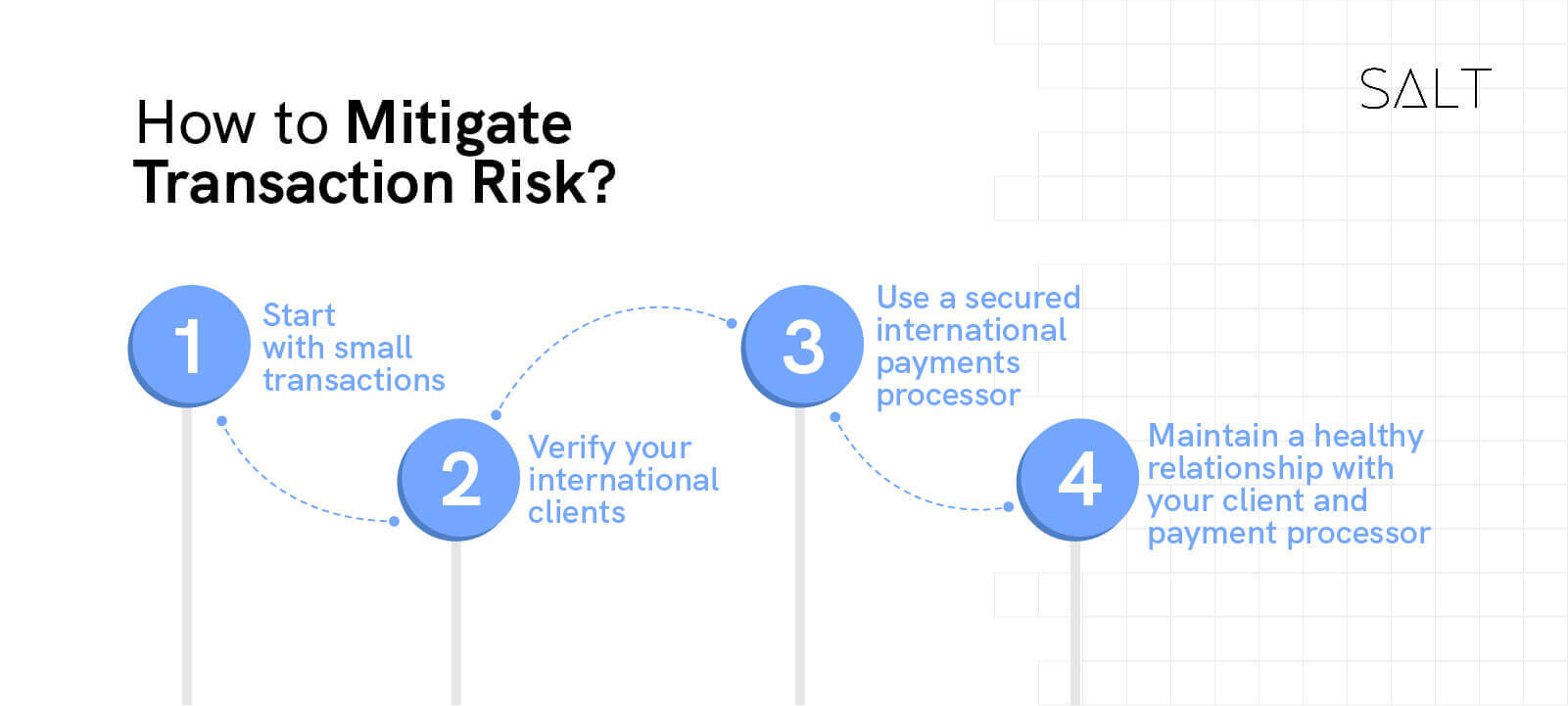
1. Take it easy at first
Don't go into major international deals without first testing the waters. Begin with a tiny purchase or sale to gauge the other party's reliability.
2. Carry out your homework
Have you taken the rudimentary steps to verify your International clients or partners financial stability? We highly recommend that you stop by their office.
3. Make use of secure International Payments options.
It would help if you took precautions unless your connection for International Payments with your foreign partner has been long-standing and secure. National Bank is here to advise you on the safest and most convenient option. Letters of credit and advance payments may be arranged.
4. Form a meaningful relationship
The value of a reliable and trustworthy business connection cannot be overstated. Investing in solid relationships with your business's allies and customers is essential. You might have the most ironclad contract in the world, but if you don't know and trust your International Customers, they can decide they don't want to pay.
Advantages of Transaction Risk Management
Effective transaction risk management contributes to a culture that fosters sound risk management practices across the board. The following are elements of, and should be promoted by, a solid transaction risk reduction program:
An in-depth review by the powers-that-be
Various market exposure and risk policies monitor political unrest in various countries.
Currency-denominated assets and debts should be subjected to regular historical simulations.
Regulation of the economy to keep things in order across markets
Consistent auditing and internal control procedures
Conclusion
There is a risk of transaction for each transaction that anticipates receiving cash from a deal when the amount received might fluctuate wildly. There is often a safe and sound system in place at most institutions to deal with transactional risk. However, the Asian Crisis taught us the need to maintain a healthy equilibrium between credit and liquidity.
If your organization is vulnerable to foreign exchange fluctuations, you must establish a fair tolerance threshold and clearly define what constitutes severe exposure. Detail the processes and policies, and then cautiously put them into effect.


