Some people enquire about the meaning of the Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC), the Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC), and the differences between the Bank Realisation Certificate and the Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate.
Both are, strictly speaking, certificates that the authorised dealer bank issues to clients to accept payments from other countries. An approved bank gives both the BRC and FIRC to clients who receive money or conduct business abroad.

Now let's compare the two ideas in this blog.
Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC)
A Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC) is a document that serves as verification of a company's international exporting activities. This paper is essential for a client who wishes to trade benefits under the foreign trade policy in India. The DGFT, RBI, FEMA, Customs, and other departments of the Indian government oversee commerce.
Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC)
The word "FIRC" may have come up when money is sent from other nations to India using online payment methods like PayPal. The approved bank in India that receives the money makes a FIRC request.
It is a security document that serves as documentation for remittances that enter India. This document can be used as proof by a receiver in India who gets money through their business or a cash transfer from abroad. This certificate is crucial if you want to receive cross border payments from another country.
A document known as a Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC) is used to show a cross border payment has been received in India. Beneficiaries who receive inward remittances in India must have this certificate. Most statutory bodies view it as documentary evidence demonstrating the validity of the foreign cash the beneficiary received.
The RBI and FEDAI (Foreign Exchange Dealers Association of India) regulations limit the granting of FIRCs in India to Authorised Dealer Category I (AD) institutions.
Learn in detail why RBI needs BRC and FIRC In Your International Transactions.
Where are the BRC and FIRC used?
A bank often issues BRCs to its clients engaged in the export industry with each shipment of export revenues. Numerous organisations that promote exports offer incentives, exemptions from import duties, and other forms of financial support to exporters. To obtain these incentives, exporters must submit export documentation as required by these authorities. In addition to the copy of the shipping bill, the carrier's Mate Receipt, and the customs-authorised ARE-1, further evidence of exports includes the Bank Realisation Certificate (BRC) provided by the particular bank that received the exporter's foreign payment.
FIRC and its issuance are primarily subject to the control of two organisations, namely:
Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
Foreign Exchange Dealers Association of India (FEDAI)
When beneficiaries receive an overseas payment from a country other than India, only an authorised dealer may credit it to the beneficiary's account, according to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the Foreign Exchange Dealers Association of India (FEDAI).
An authorised dealer is a person or business that has received authorisation from the Reserve Bank of India to conduct transactions in foreign money or foreign securities following the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA). If the beneficiary's bank is not an AD, the inbound remittance is sent to the recipient's account through an approved dealer. Based on the information supplied by the receiver upon receipt of money, the AD banker will issue a FIRC describing the purpose of receipt, such as towards equity investment, advance against export of services or commodities, capital expenditure, etc.
How to acquire BRC?
Below are the steps to claim your BRC certificate online:
Visit the DGFT website and sign up for an account on the eBRC programme.
To upload the file, select the BRC upload option. Please choose the appropriate file from the file system and then upload it.
The server will present the results in either XML or tabular format, depending on the user's preferences, once the user and data have been confirmed.
To take advantage of the export incentives, provide eBRC as evidence of export.
When exporting services, submit the eBRC with an integrated GST or input tax credit refund application.
How Can You Claim FIRC?
The FIRC can be claimed by visiting the bank itself.
The following information about the transaction must be included in a letter to the bank to seek a FIRC:
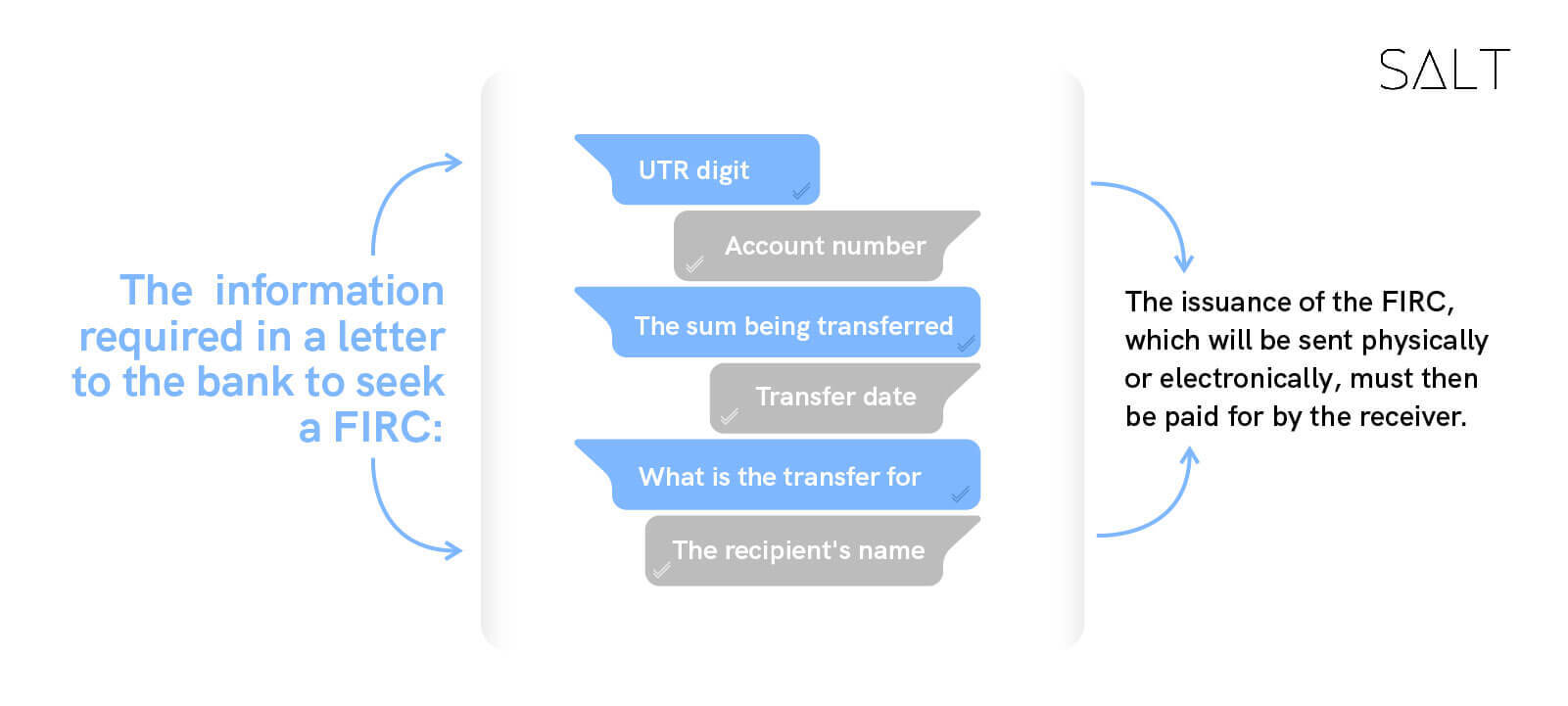
The issuance of the FIRC, which will be sent physically or electronically, must then be paid for by the receiver.
Some more differences between BRC and FIRC
Many may still need clarification on the distinction between the FIRC and the BRC, which is usually ambiguous. However, the following differences may help you understand the same clearly.
The beneficiary's AD institutions provide BRC and Foreign Inward Remittance certificates to customers who receive cross border payments.
The beneficiary's bank specifically issues the Bank Realisation Certificate in conjunction with the export of goods. Each time an export revenue shipment is made, the bank releases a BRC.
The bank issues a Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate and accepts foreign payments. This amount may be used as export compensation or as a down payment for air or sea freight. Even payment for advisory services is a possibility.
How Salt helps you procure FIRC?
As was already indicated, the FIRC is also quite significant in terms of inward remittances received in India. Therefore, it is vital and imperative for the beneficiaries to follow up with the banks and get their FIRC issued as soon as possible after the inward remittance has been credited.
Users of Salt can get FIRC for inward remittances received through us. Register right now to avail our neobanking services!


