Say you are engaged in a business of exporting goods from India to other countries or you are an India based freelancer providing services abroad. Then, your profession involves cross border money transfers as you receive your payments from abroad. Here, you must have a document called the FIRC or the Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate, which is a piece of paper acting as a proof of the international payments received.
The process of getting this FIRC involves the beneficiary (the receiver of foreign remittance) applying for it once he/she receives the transfer in his/her bank account. The purpose of it has to be stated with clarity and thereafter on the basis of the information given, the Authorised Dealer (AD) of the RBI, which is typically the bank through which the intentional payments are credited into your account, will provide you with the FIRC.
In this post, we review why a FIRC is important.
Types of FIRC
An Authorised Dealer (AD) issues the following two types of FIRC-
Physical Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC)
If your business is involved in inward remittances against Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Foreign Institutional Investment (FII) (which involve international payments only through banking channels under the guidelines of the RBI), then a physical FIRC will be issued.

Electronic Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (e-FIRC)
The ADs have to report the proof of all the inward remittances to the Export and Data Monitoring Systems (EDPMS) and thereafter they issue the e-FIRC, which is the electronic version of the physical FIRC.
The receipt of payment or any other advances/outstanding transfers to the exporter of the goods/services is to be given to the bank by the beneficiary which is then uploaded to the EDMPS.
An inward remittance (IRM) number is then generated for the issuance of the e-FIRC that comes to the beneficiary’s account within a week or two from the date on which the foreign currency was credited to the account of the beneficiary through a cross border money transfer.
Foreign Inward Remittance Advice (FIRA)
If the foreign transfer received does not fall in either of the above categories, then the business can apply for this type of advice which is basically a certificate of inward remittance acting as a legal proof of the international payments received by the exporting company or the freelancer in exchange for his/her services.
The request for FIRA is made by the beneficiary to the partner bank that has processed the cross border money transfer and details like account number, amount of transfer, intent of transfer along with the transaction date has to be provided.
Post submission of the request, the details mentioned above are verified by the bank and uploaded on the EDMPS. An IRM number is then generated on the portal from which the beneficiary can later download the Advice.
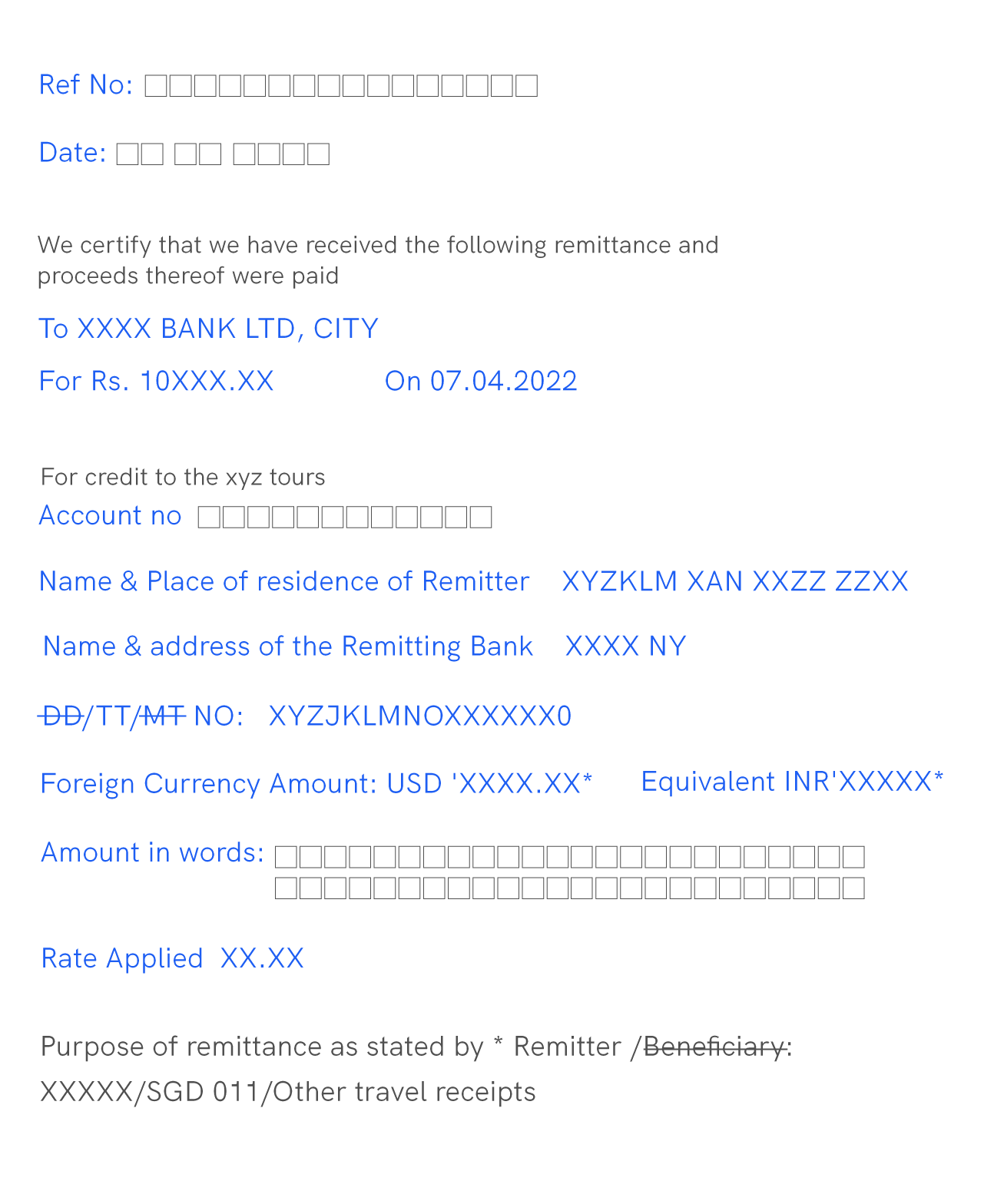
Information contained in the FIRC
A Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate has the following details:
Name of Beneficiary/Exporter
Mode of payment
Payee’s name and address
Name and address of the bank authorising the transaction
Cheque number or telegraphic transfer (TT) or demand draft (DD) number
The FDI amount in the foreign currency
The equivalent amount mentioned in rupees, in numbers as well as in words
The name of the recipient
The foreign exchange rate prevalent
the purpose behind the inward remittance like share transfer or export
The Importance of FIRC
Coming to the topic at hand, why is FIRC important anyway?
It is a legal proof of the inward remittance of foreign exchange which the RBI has to closely monitor. The FIRC provides the RBI with the details of all transactions involving receipt of payments from abroad. The ADs are required to report these remittances on the EDMPS which is the online application allowing all the Indian-authorised banks to disclose the inward remittances of foreign currency to the Reserve Bank of India, thereby making the system of cross border money transfer more transparent.
If you are an exporter and no service tax is levied on the export of your services as mentioned in the guidelines of export of services, then the FIRC acts as an indispensable proof of the transactions and helps you in getting tax benefits in areas in which you are entitled. By showing the FIRC, you can claim the relaxations in service tax (on the provision of certain services) but without producing it you cannot claim any benefits.
FIRC is extremely important when shares are issued to a foreign entity or a foreign person as it serves as a proof of the receipt of the share application money from them. It also provides a proof in cases where a resident Indian transfers his shares to a non resident person or a foreign entity and receives the required amount as purchase consideration.
It is also one of the crucial documents that have to be submitted as proof to the Director General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) in cases of export promotion schemes like Export Promotion Capital Goods (EPCG) and advanced licensing requirements.
Conclusion
As we have seen, a Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate is an extremely important document when it comes to inward remittances from foreign banks and that is why an exporter or a freelancer should follow up with the bank to obtain this certificate with every inward remittance.
We hope this post was helpful in explaining the relevance of FIRC to you. We at Salt Fintech provide you with FIRC for inward remittance transactions. Sign up with us today to accelerate cross border money transfers to your Indian bank account in as many as six currencies, that too within 24 hours!
FAQS - Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC)
Which bank is authorised to issue an FIRC when the inward remittance is transferred through more than one bank account?
As per RBI’s clarifications and the provisions under FEMA, the first bank in India that receives the inward remittance in foreign currency has to issue the Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate because it has the requisite details of the overseas bank that has remitted the foreign exchange.
What is the difference between BRC and FIRC?
Both the Bank Realisation Certificate and Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate are issued by the AD, but in contrast to the FIRC which is given against the receipt of international payments, the BRC is issued against any specific documents.


